📚 Chapter1: - Introduction
If you want to read more articles about Computer Vision, don’t forget to stay tuned because we reach end to end:) click here.
Sections
What is mean by Vision
What is computer Vision?
What is Computer Vision NOT?
How does computer vision work?
History of computer vision
Section1- What is mean by Vision
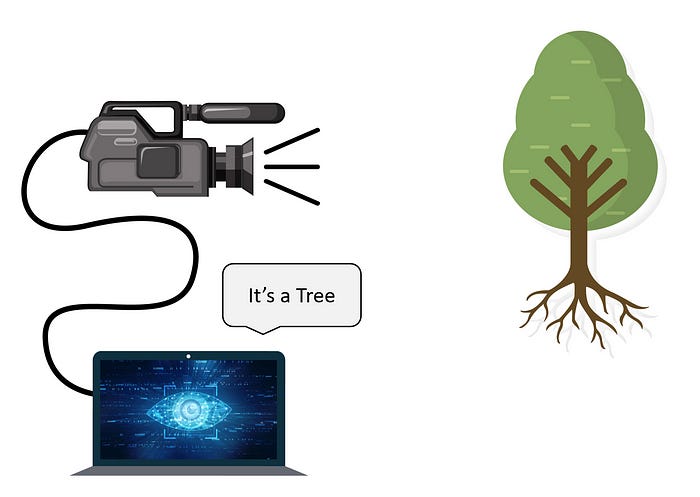
Computer Vision is about discovering from images what is present in the scene and where it is
Section2- What is computer Vision?
Def: In Computer Vision a camera (or several cameras) is linked to a computer. The computer interprets images of a real scene to obtain information useful for tasks such as navigation, manipulation and recognition
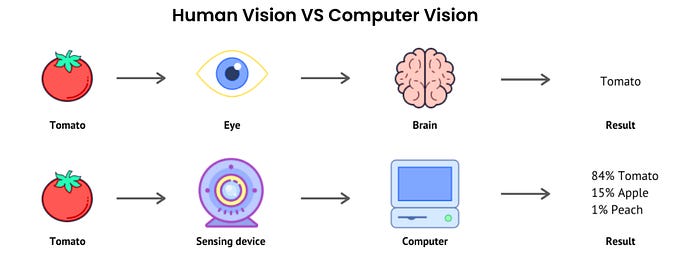
Definition: Computer vision is a field of artificial intelligence that trains computers to interpret and understand the visual world. Using digital images from cameras and videos and deep learning models, machines can accurately identify and classify objects — and then react to what they “see.”
Defination1: “Computer vision is an interdisciplinary scientific field that deals with how computers can gain high-level understanding from digital images or videos. From the perspective of engineering, it seeks to understand and automate tasks that the human visual system can do” [1]
Definition 2:“Computer Vision is just a field of AI that enables computers or machines to see and understand the world and the things in it” [1]
Definition 3-GPT: Computer vision is a field of study in computer science and artificial intelligence that focuses on enabling computers to interpret and understand visual data from the world around us. It involves developing algorithms and techniques that allow computers to analyze and make sense of images and videos, just like humans do.
Well, there’s a couple of ways of thinking about it. where he talks about every picture tells a story. And one way of thinking about computer vision is the goal is to interpret images. That is, say something about what’s present in the scene or what’s actually going on. So, what we’re doing is, we’re going to take images in, and what’s going to come out is something that has some meaning to it. That is, we’re going to extract, we’re going to create some sort of interpretations, some sort of an understanding of what that image is representative of. This is different, many of you may have some exposure to image processing, which is the manipulation of images. That’s images in and images out. And we’ll talk a little bit about that because you use image processing for per, for computer vision. But fundamentally computer vision is about understanding something that’s in the image [3].
Section 3- What is Computer Vision NOT?
Image processing: image enhancement, image restoration, image compression. Take an image and process it to produce a new image which is, in some way, more desirable. • Computational Photography: extending the capabilities of digital cameras through the use of computation to enable the capture of enhanced or entirely novel images of the world. (See my other cours
Section 4-How does computer vision work?
Computer vision technology tends to mimic the way the human brain works. But how does our brain solve visual object recognition? One of the popular hypothesis states that our brains rely on patterns to decode individual objects. This concept is used to create computer vision systems [5].Computer vision algorithms that we use today are based on pattern recognition. We train computers on a massive amount of visual data — computers process images, label objects on them, and find patterns in those objects. For example, if we send a million images of flowers, the computer will analyze them, identify patterns that are similar to all flowers and, at the end of this process, will create a model “flower.” As a result, the computer will be able to accurately detect whether a particular image is a flower every time we send them pictures.[5]
Computer vision works in three basic steps:
1- Acquiring an image
Images, even large sets, can be acquired in real-time through video, photos or 3D technology for analysis.
2- Processing the image
Deep learning models automate much of this process, but the models are often trained by first being fed thousands of labeled or pre-identified images. Computer vision algorithms are based on pattern recognition. We train our model on a massive amount of visual(images) data. Our model processes the images with label and find patterns in those objects(images).
3- Understanding the image
The final step is the interpretative step, where an object is identified or classified.
Example
For example, If we send a million pictures of vegetable images to a model to train, it will analyze them and create an Engine (Computer Vision Model) based on patterns that are similar to all vegetables. As a result, Our Model will be able to accurately detect whether a particular image is a Vegetables every time we send it [1].
Section 5-History of computer vision
1950s,
Early experiments in computer vision took place in the 1950s, using some of the first neural networks to detect the edges of an object and to sort simple objects into categories like circles and squares [1].
1970s
In the 1970s, the first commercial use of computer vision interpreted typed or handwritten text using optical character recognition. This advancement was used to interpret written text for the blind.
1990s
As the internet matured in the 1990s, making large sets of images available online for analysis, facial recognition programs flourished. These growing data sets helped make it possible for machines to identify specific people in photos and videos.
🌟 Our Valued Sponsors
We extend our heartfelt thanks to our incredible sponsors for their generous support and commitment to our mission. Their contributions make it possible for us to continue developing open-source educational content, AI learning tools, and community-driven projects.
💼 Our Sponsors
InnoviTechs IT Services- Driving Digital Transformation and Business Growth
Your support helps us:
-
Create free tutorials, guides, and datasets for learners worldwide 🌍
-
Maintain research repositories and AI projects 📚
-
Host workshops, webinars, and community learning events 💬
-
Encourage students and educators to explore Data Science, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning 🚀
🙌 Become a Sponsor
Join these amazing organizations in supporting our community!
You can become a sponsor through GitHub Sponsors or reach out via mushtaqmsit@gmail.com for partnership and bank sponsorship options.
📩 What’s Next?
Liked this tutorial?
👉 Subscribe to our newsletter for more Python + ML tutorials
👉 Follow our GitHub for code notebooks and projects
👉, Computer Vision: Enroll for Full Course to find notes, repository etc.
👉, Deep learning and Neural network: Enroll for Full Course to find notes, repository etc.
🎁 Access exclusive Supervise Leanring with sklearn bundles and premium guides on our Gumroad store: From sentiment analysis notebooks to fine-tuning transformers—download, learn, and implement faster.
💬 Drop a comment below if you have questions or want to share your results!
Sources
1-Introduction of Computer Vision
1-What Is Computer Vision — A very Simple Explanation (Episode 2 | CVFE)

i need feedback
ReplyDelete